How to operate a drone safely and effectively opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision inspections. Understanding the fundamentals of drone operation, including pre-flight checks, control mechanisms, and safe flight procedures, is crucial for both novice and experienced pilots. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the skies responsibly.
This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from basic controls and pre-flight safety checks to advanced flight techniques and legal considerations. We’ll explore different flight modes, camera settings, troubleshooting common issues, and essential emergency procedures. Whether you’re a beginner looking to take your first flight or an experienced pilot seeking to refine your skills, this resource offers valuable insights and practical advice to enhance your drone piloting journey.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and responsible drone operation. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, damage to the drone, and potential harm to people or property. This section details the essential steps and safety regulations to follow before each flight.
Pre-Flight Inspection
Before every flight, perform a comprehensive inspection of your drone. This includes checking the battery level, ensuring propellers are securely attached and undamaged, and verifying a strong GPS signal. A visual inspection of the drone’s body for any damage is also recommended. Confirm that all components are functioning correctly before powering on.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount for responsible drone operation. The following table Artikels key regulations and recommendations to consider:
| Regulation/Practice | Description | Importance | Consequences of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Check Battery Level | Ensure sufficient battery power for the planned flight duration, accounting for safety margins. | Prevents mid-flight power loss. | Crash, potential damage, and injury. |
| Maintain Visual Line of Sight | Keep the drone within your direct visual range at all times. | Ensures control and prevents loss of orientation. | Loss of control, potential accidents. |
| Avoid Flying Near Airports or Airspaces | Check airspace restrictions using apps like B4UFLY or AirMap before flying. | Ensures safety of manned aircraft. | Legal penalties, potential collisions. |
| Respect Privacy | Do not fly over private property without permission. | Protects individual privacy rights. | Legal repercussions, potential lawsuits. |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section explains the basic controls, GPS-assisted flight, and various flight modes.
Basic Drone Controls

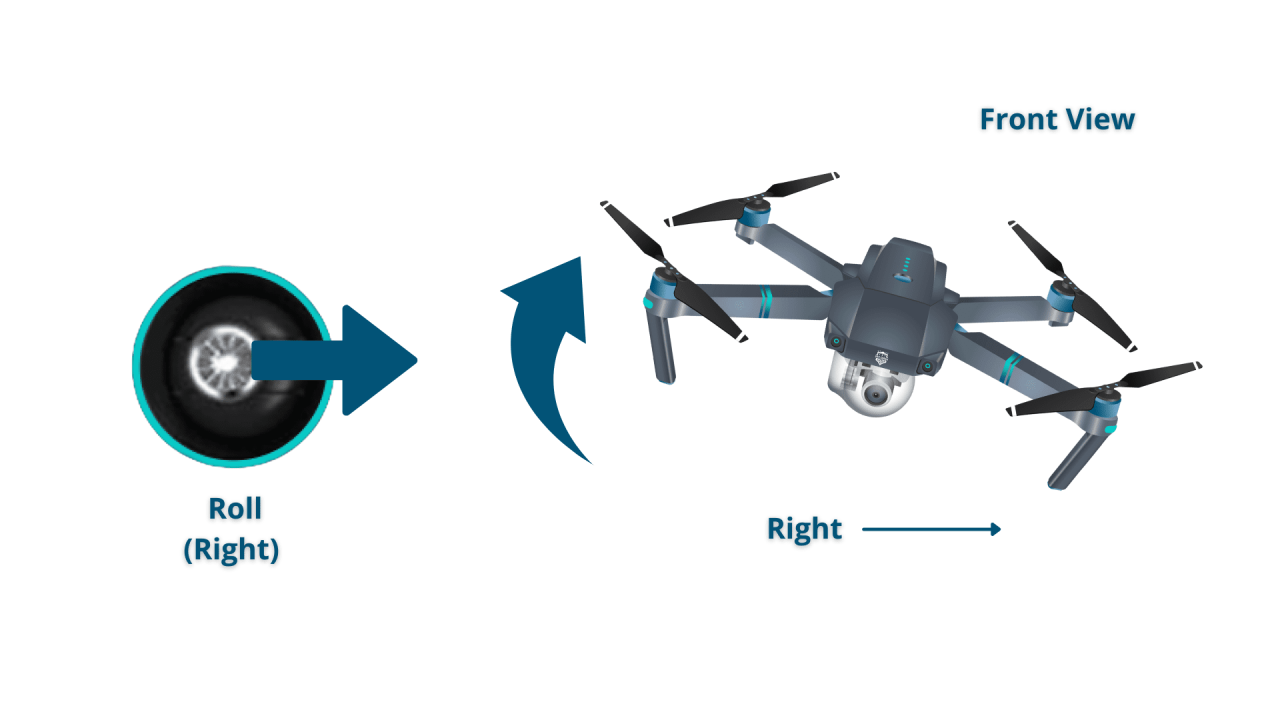
Most drones utilize a control system based on four primary axes: throttle (up/down), yaw (rotation), pitch (forward/backward tilt), and roll (left/right tilt). These controls are typically mapped to joysticks on a remote controller. Mastering these controls is essential for smooth and precise maneuvering.
GPS-Assisted Flight and Flight Modes
GPS-assisted flight utilizes satellite signals to determine the drone’s location and altitude, enabling features like altitude hold, position hold, and return-to-home (RTH). Altitude hold maintains a constant altitude, position hold keeps the drone in a fixed location, and RTH automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point. Transitioning between modes usually involves pressing a button or switching via a menu on the controller.
Examples of Mode Transitions
For example, to switch from position hold to altitude hold, you might press a dedicated button on the controller. Similarly, initiating RTH typically involves pressing a specific button or selecting the function on the controller’s screen.
Taking Off, Flying, and Landing
The procedures for taking off, flying, and landing a drone are crucial for safety and to prevent damage. This section Artikels a step-by-step guide for each phase of flight.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
A safe takeoff involves a series of careful steps to ensure a smooth and controlled ascent.
- Perform pre-flight checks.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for GPS signal acquisition.
- Slowly increase throttle to initiate ascent.
- Maintain visual line of sight.
Maneuvering the Drone
Precise hovering and controlled movements are achieved through skillful manipulation of the drone’s controls. Practice is key to mastering smooth and accurate maneuvers. Start with small, controlled adjustments to get a feel for the drone’s responsiveness.
Safe Landing Procedure
A safe landing requires a methodical approach to ensure a smooth and controlled descent.
- Begin descent slowly, reducing throttle gradually.
- Maintain a stable hover close to the ground.
- Gently lower the drone until it touches down.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography: How To Operate A Drone
Many drones are equipped with high-quality cameras capable of capturing stunning aerial footage. Understanding the camera’s features and settings is crucial for achieving professional-quality results.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. Learning the fundamentals is key, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced techniques. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the regulations.
Drone Camera Features and Functions
Typical drone cameras offer features such as adjustable zoom, video recording capabilities, and image stabilization. Some drones also have advanced features like obstacle avoidance and automated flight modes for specific shots.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture significantly impact image quality. Higher ISO values increase sensitivity to light but can introduce noise. Shutter speed controls motion blur, while aperture affects depth of field.
Flight Plan for Aerial Shots

A well-planned flight path is essential for capturing desired shots. For panoramic views, consider flying in a circular or sweeping motion. For close-ups, plan a steady approach to the subject, maintaining a safe distance.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful preparation, drone operation can encounter problems. Understanding common issues and their solutions is essential for efficient troubleshooting.
Common Drone Problems and Troubleshooting Steps
| Problem | Troubleshooting Steps | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Check battery level, charge battery. | Low battery charge. | Charge the battery fully. |
| GPS Signal Loss | Check GPS signal strength, move to an open area. | Obstructions, weak signal. | Relocate to an area with clear sky view. |
| Motor Malfunctions | Check motor connections, inspect propellers. | Loose connections, damaged propellers. | Tighten connections, replace damaged propellers. |
| Controller Disconnection | Check controller batteries, check connection. | Low batteries, interference. | Replace batteries, move away from interference. |
Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the drone and inspecting components, is crucial for preventing issues and extending the drone’s lifespan. This includes checking for loose parts, cleaning propellers, and inspecting the battery.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to all relevant laws and regulations. This section discusses the importance of legal compliance.
Drone Regulations and Permits
Drone regulations vary by location. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific laws and regulations in your area before operating a drone. This may involve obtaining necessary permits or licenses, depending on your intended use and location.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Violation of drone regulations can lead to significant consequences, including hefty fines, legal action, and even criminal charges. Responsible operation is not merely a suggestion; it is a legal requirement.
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques
Beyond basic operation, advanced flight techniques allow for creative aerial photography and videography.
Cinematic Shots and Waypoints
Techniques like orbiting, tracking shots, and the use of waypoints and pre-programmed flight paths enable the creation of professional-quality aerial footage. Waypoints allow for precise control over the drone’s flight path, making complex shots easier to achieve.
Drone Model Comparison
Different drone models cater to specific needs. Some are optimized for photography, others for videography, and some for inspection tasks. Consider factors such as camera quality, flight time, and features when choosing a drone.
Drone Battery Management and Safety
Proper battery management is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation. This includes charging, storage, and recognizing signs of battery failure.
Battery Charging and Storage
Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow instructions carefully. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures.
Signs of Battery Failure
Signs of a failing battery may include reduced flight time, abnormal heating, or swelling. If you notice any of these signs, replace the battery immediately.
Battery Safety Precautions
- Never leave batteries unattended while charging.
- Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries.
- Handle batteries with care, avoiding damage to the terminals.
Emergency Procedures
Despite careful planning, emergencies can occur. Knowing how to respond appropriately is crucial.
Emergency Response Steps, How to operate a drone
- If you lose control, attempt to regain control using the emergency stop function (if available) or carefully lower the drone to the ground.
- If a crash occurs, assess the damage and ensure personal safety before attempting recovery.
- If a malfunction occurs mid-flight, attempt to land the drone safely in a clear area. If this is not possible, initiate RTH if available.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. By diligently following safety protocols, understanding your drone’s capabilities, and continuously honing your skills, you can unlock the full potential of this remarkable technology. Remember, responsible drone operation ensures both your safety and the safety of others, allowing you to enjoy the thrill of flight while respecting the airspace and surrounding environment.
Safe flying!
Clarifying Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are excellent for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes. Look for models with intuitive controls and robust safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass regularly, especially before each flight, ensures accurate navigation. The frequency depends on the drone model and usage but is generally recommended before every flight session.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires understanding regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical exercises and troubleshooting tips, please refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Proper training ensures safe and responsible drone piloting, ultimately enhancing your aerial experience.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower altitude and attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, execute a safe landing procedure and troubleshoot any potential issues.
How long does a typical drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, usage, and environmental factors. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, but always check your specific drone’s specifications.